ETA Factory
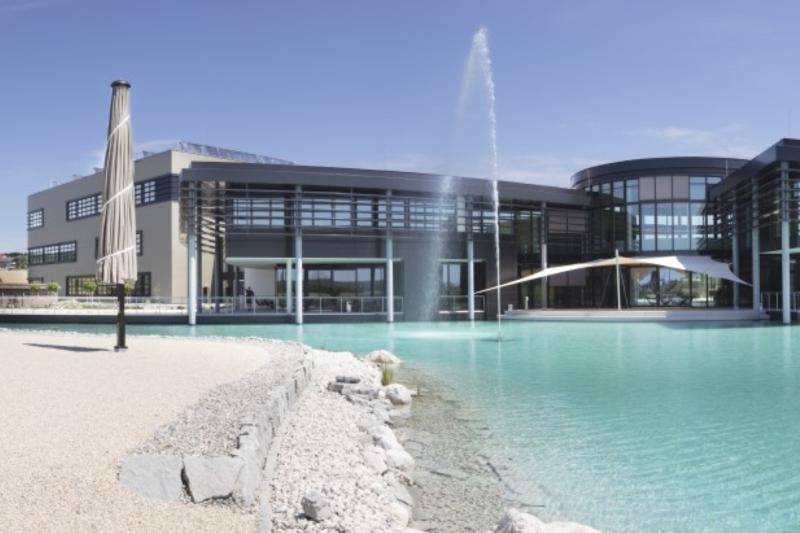
The ETA factory of TU Darmstadt is located in the Lichtwiese campus and was completed in March 2016. Since then, the model factory has been used in particular for research in the field of "energy efficiency in the industrial sector" and is intended to represent a milestone in the scientific development of innovative technologies for increasing energy efficiency.
TU Darmstadt, Department V Construction Management and Technical Operations
March 2016
122 kWh/m²a
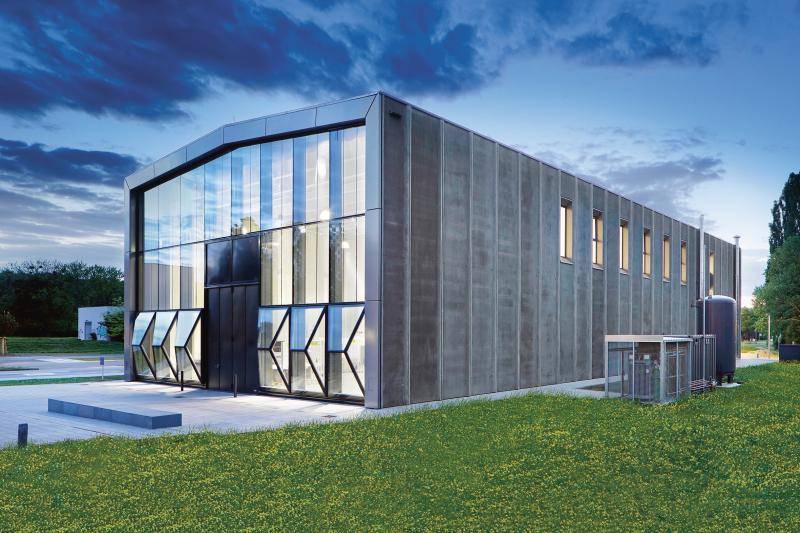

The ETA factory of TU Darmstadt is located in the Lichtwiese campus and was completed in March 2016. Since then, the model factory has been used in particular for research in the field of "energy efficiency in the industrial sector" and is intended to represent a milestone in the scientific development of innovative technologies for increasing energy efficiency.
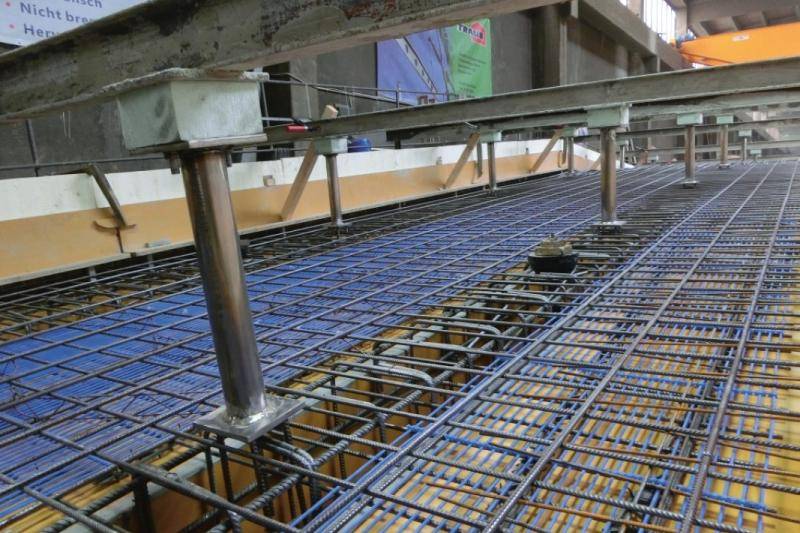
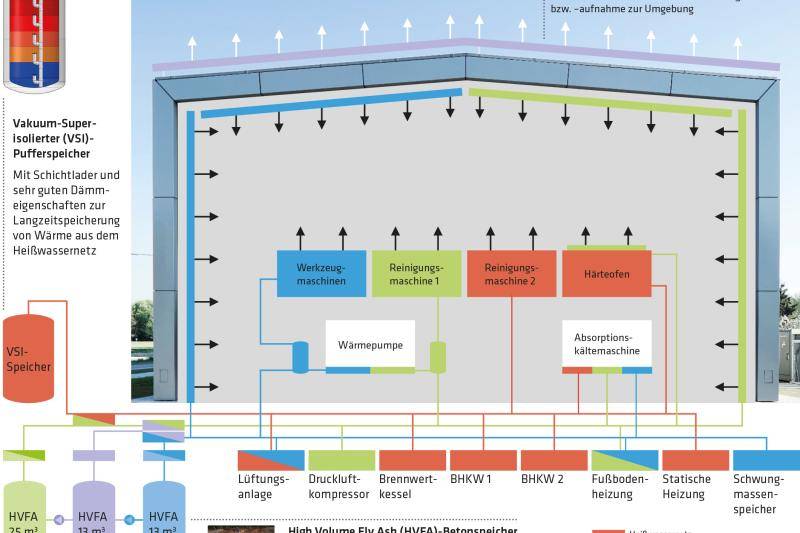
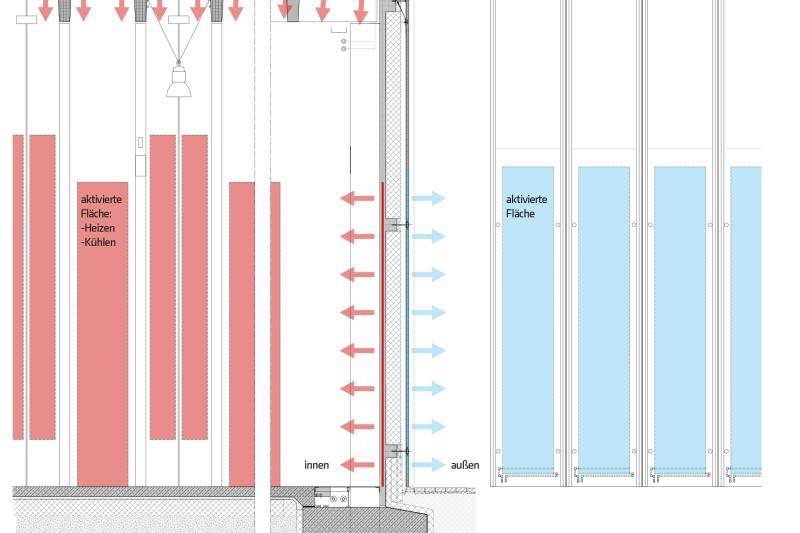
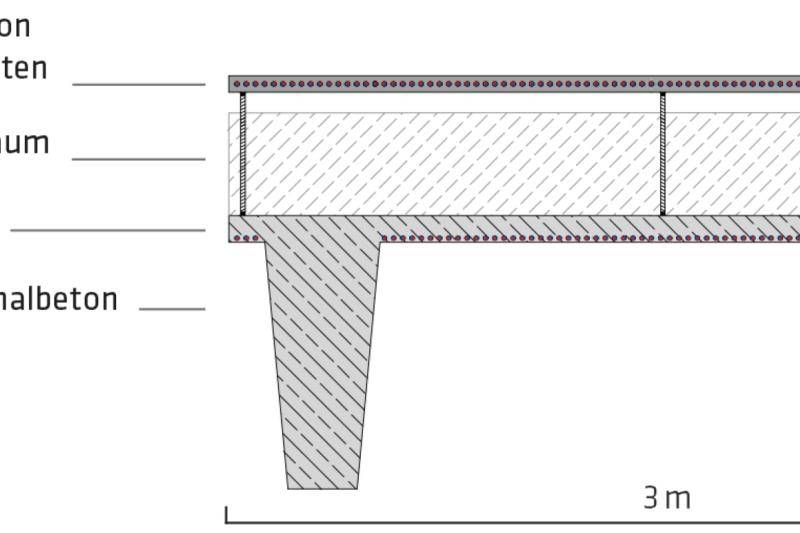
The building shell of the ETA factory was produced in solid construction as a rear-ventilated curtain wall made of concrete in combination with mineral foam (MF), which ensures an almost single-variety structure of the building shell. Capillary tube mats made of polypropylene, through which a water-glycol mixture flows, were embedded in the two concrete layers (inner shell: normal concrete and outer shell: mrUHPC). The interior and exterior elements of the facade are linked via the capillary tube mats and are also connected to the three thermal-hydraulic networks of the building. In addition, energy storage can be provided in external concrete storage tanks. This thermal networking enables interaction between the building envelope and production processes. In this way, the LowEx waste heat that can no longer be used in production processes is dissipated via the building envelope in summer and used to heat the building in winter, thus increasing the efficiency of the entire production line. The incorporation of low-exergy waste heat into the building technology can only be realized with the aid of the large heating or cooling surfaces for building and machine cooling.
(Text source: TU Darmstadt)